UPM RISC-V processor with custom CGRA-based extensions
| ID: R2 | Licence: Solderpad Hardware Licence v2.1 | Owner: UPM | Contacts: joseandres.otero@upm.es alfonso.rodriguezm@upm.es |
| Short Description | Multi-grain CGR Array (CGRA) tightly coupled with an open-source RISC-V processor through custom ISA extensions to support 1) automatic SW-to-HW code offloading using HW composition, 2) Edge AI capabilities in the RISC-V ecosystem. |
| Require | Application code with hardware acceleration requirements at the edge. |
| Provide | Acceleration infrastructure at the edge. |
| Input | Binary files for processor (application executable), CGRA accelerator (CGRA configuration bitstream), and the static configuration bitstream for the FPGA. |
| Output | Heterogeneous and hardware-accelerated execution of the application. |
| MYRTUS layer | Edge |
| TRL@M0 | 3-4 |
| TRL@M36 | 5 |
General description
A multigrain reconfigurable CGRA overlay for FPGAs loosely coupled with a host processor (Arm-based) via a standard memory-mapped interface. Support for a reduced set of integer arithmetic and logic operations within its core Processing Elements (PEs), and use of different granularity levels for FPGA reconfiguration (i.e., coarse to modify large chunks of the fabric, medium to compose regular 2D computing structures on the fabric, and fine to only modify LUT contents to change PE functionality).
MYRTUS Extension/Contribution
Integration of the CGRA on the datapath of an open-source RISC-V processor core to provide hardware-accelerated custom ISA extensions as an alternative to the memory-mapped approach. Development of AI-oriented PEs (e.g., fixed- and floating-point arithmetic) and the exploration of heterogeneous CGRA distributions (i.e., using different PEs in each position in the 2D grid, for instance to include internal scratchpad memories or mixed precision arithmetic).
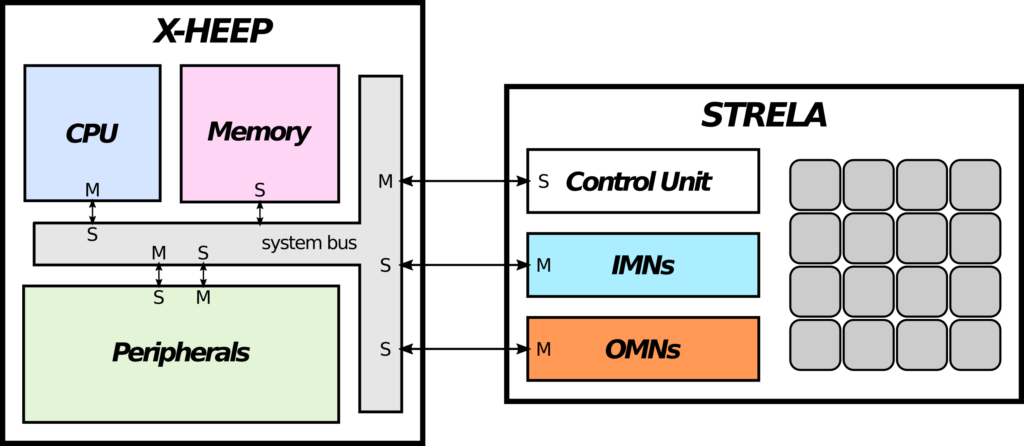
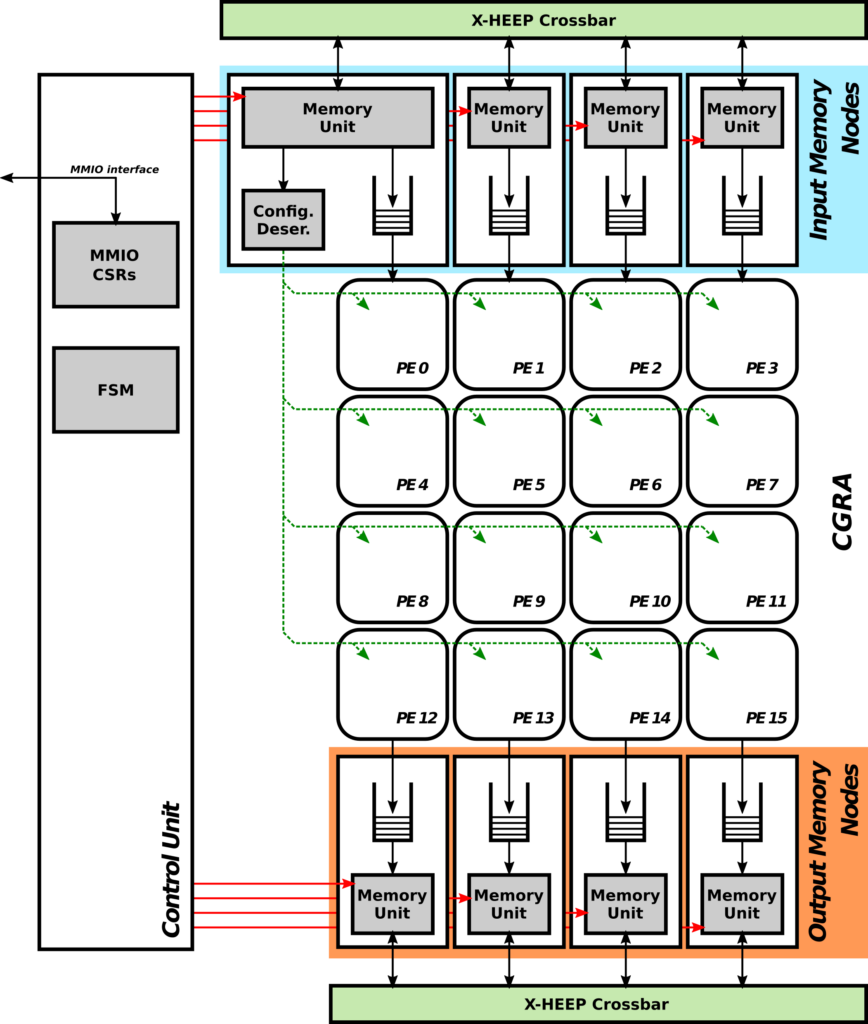
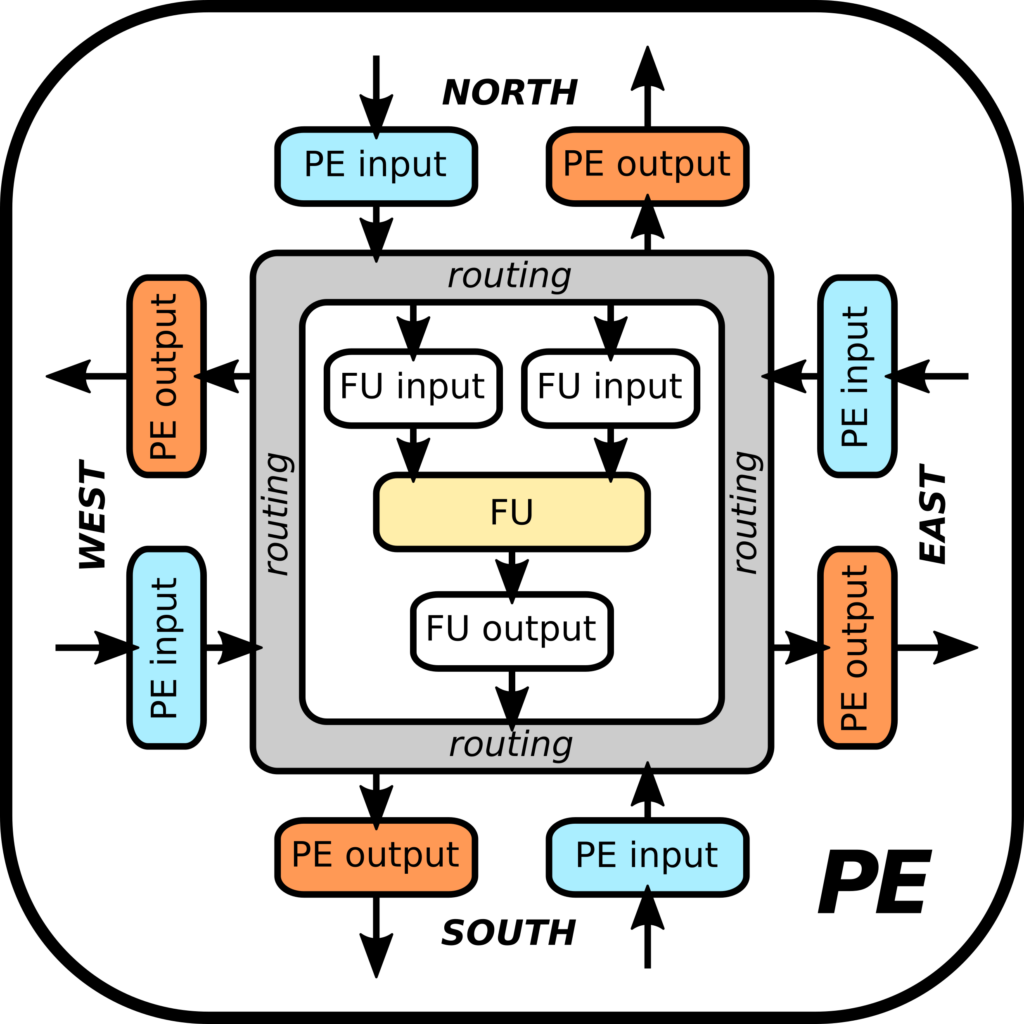
Plans and Expectation
Assessment Plan@M18:
RTL simulation of the integrated CPU+CGRA computing infrastructure, using custom assembly instructions to properly exercise the accelerator with manually mapped application benchmarks (e.g., PolyBench). Synthesis and implementation on multiple FPGA devices, changing the spatial distribution and processing capabilities of the CGRA. Initial exploration of the heterogeneous version.
Expected Results@M18:
Improved energy efficiency and performance metrics of the application benchmarks running on the CGRA fabric with hand-made mapping, which are to be assessed both at simulation level and on the target FPGA boards. Comparison of offloading overheads for both memory-mapped and extended-ISA flavors of the CGRA.